PLC Field Communications
Choosing a Field Communication
Field Communication concepts
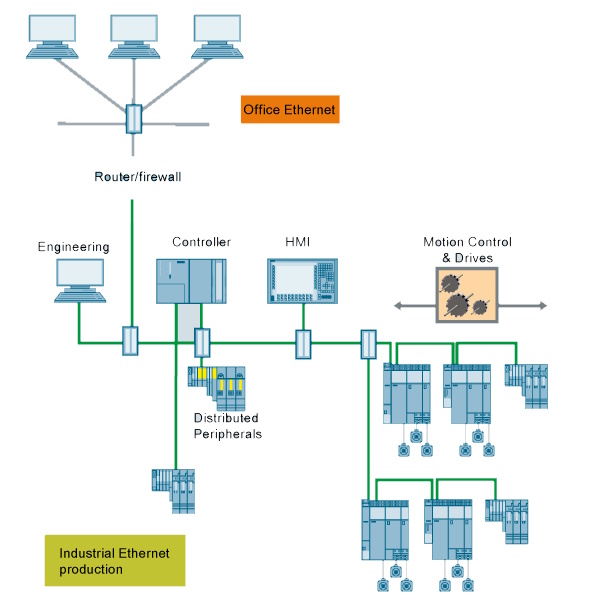
Field communication has advantages and disadvantages compared with hard wired IO loops.
- Less Cabling. Field communication reduces cabling as well as the infrustructure required for the cabling such as cable trays, cable tray supports and labour required to install the cables and cable tray.
- Higher accuracy. Analog information obtained from the field does not need any conversion or scaling. An analog input of 0-20mA, that is hardwired to a 16 bit analog input channel is converted by the hardware to a number ranging from 0 to 65536. The anaog value then needs to be converted in software to the range of the transmitter. But when using field busses, the value you get is the actual value.
- More data. When using a field busses, it is normal to read more information from field devices than just the process vales. Status and health values are available with no additonal cables required.
- PLC to Smart devices. Of course a widely used function of field bussed is the ability to control more complicated devices. An example would be for electrical switchgear where currents, voltages, power, power factor, faults, trips codes, number of stop starts etc can all be read with one instruction.
- Cost saving. For most installations, field busses save on costs. This typically accepted to be around 30% saving compared to hard wired loops. This applies to larger installations
Advantages
- Less reliable. A cable fault for a hardwired tranmitter causes a single transmitter to fail. A bus fault which connects many devices can cause all the devices upstream and downstream to fail. The most important design criteria for busses is consider armoured cables and ensure proper segmentation and repeaters for stability and fault finding.
- Costly instrumnets. Field bus instruments cost more than standard instruments. Firld busses also required hardware such as splitters, repeaters, end terminators etc to operate. Small fieldbus installation are not as cost effective.
- Complexity. Loops are easy to design and fault find with simple tools such as a screwdriver and a multimeter. Busses require knowledge of network concepts to design, such as speeds and segments. Fault finding still requires a screwdriver and multimeter but requires more information about the network such as accurate network drawings, network architecture knowledge and knowledge of network voltages and terminations.
Disadvantages
- Should you use a field bus? Asolutely yes. Knowledge is power and field busses provide information in the bucket loads. This allows for better plant utilization, higher plant efficincy, greater product quality, quicker fault finding and improved asset optimization.
Conclusion
Uselful Links
Siemens Web Site
